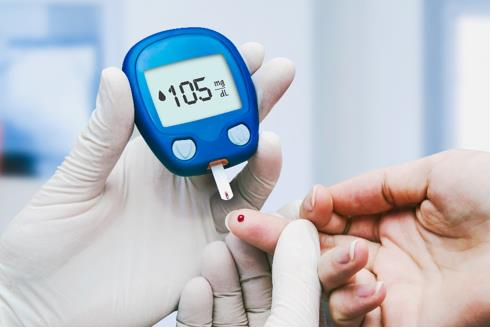
The treatment of diabetes is a comprehensive treatment of early and long-term, active and rational and individualized treatment measures. The goal is to correct metabolic disorders, eliminate symptoms, prevent or delay the occurrence of complications, reduce mortality, and ensure normal growth and development and pregnancy process. With the continuous advancement of medicine, it has a good effect on reducing the complications of diabetes. The treatment of diabetes is updated every year, in order to optimize the treatment effect and prolong the life of diabetic patients.
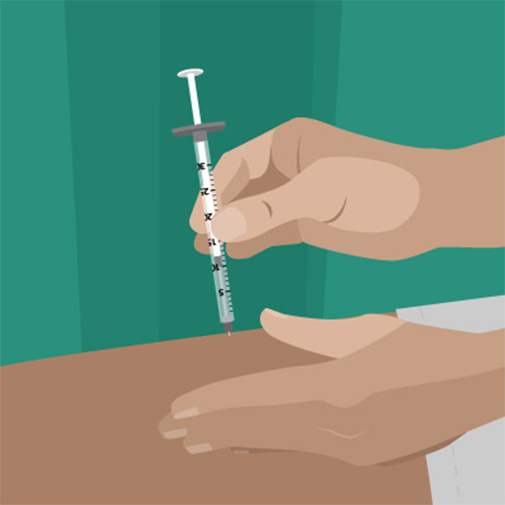
Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease caused by multiple etiologies and characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. Abnormal metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, water and electrolytes due to defects in insulin secretion and/or action (insulin resistance).