Some other causes under study include:
- An immune system reaction to excessive fatty liver tissue
- The release of toxic inflammatory chemicals (cytokines) by liver cells or fat cells
- Self-destruction (apoptosis) of liver cells
Oxidative stress, the effect of unstable molecules called free radicals
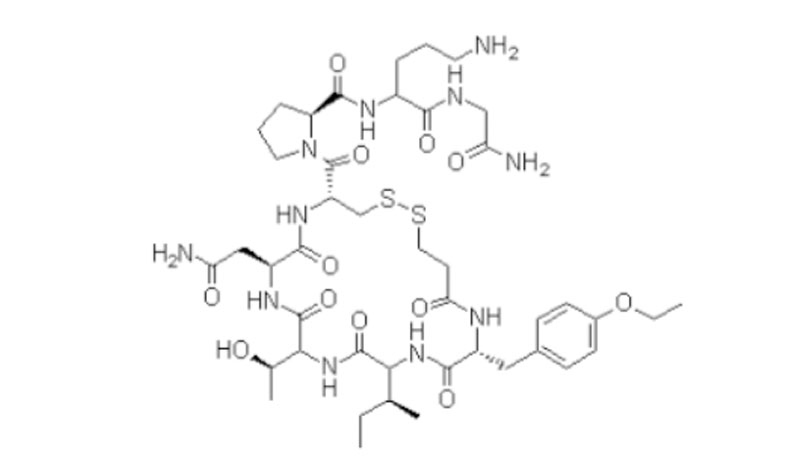
Genetics seem to contribute to NAFLD and NASH. Research has identified gene changes that might play a role, including a certain variation in the PNPLA3 gene. This gene gives cells instructions for making adiponutrin, a protein found in liver cells and fat cells. Scientists believe that a particular change in the PNPLA3 gene could cause increased fat production and decreased breakdown of fats in the liver, which may contribute to development of NASH.